Introduction:
Resistance welding
It is typically used for connecting thin plates and structures. It has various types
Working Principle:
Resistance heating at the contact surfaces causes native melting and fusion.
High currents (typically 10000 A) are applied
Features of the fundamental resistance welding process include:
The process requires relatively simple equipment;
It is easily and normally automated;
Once the welding parameters are established it should be possible
Advantages of Resistance Welding:
- They are very rapid in operation.
- The equipment can be fully automated.
- They conserve materials as no filler material, shielding gas or flux is needed.
- Skilled operators are not required.
- Dissimilar metals can be easily joined.
- A high degree of reliability and reproducibility
are often achieved.
Limitations of Resistance Welding:
- The equipment has a high initial cost.
- There are limitations to
the sort of jointswhich will be made (mostly suitable for lap joints).
- Skilled maintenance persons are needed to service the control equipment.
- Some materials require special surface preparations
before welding.
Applications of Resistance Welding:
- The major applications of
the method are within the joining of sheet steelwithin the automotive and white-goods manufacturing industries.
Types of Resistance Welding:
Different types of resistance welding process are:
Resistance Spot Welding :
Spot welding bonds alongside two or extra metal sheets, which are related in an overlapping position between a pair of welding electrodes, one fixed and one versatile.
When heavy series current is directed through these electrodes,
Advantages of Spot Welding:
- Spot welding typically comes at a lower value, each in equipment and labor.
- Spot welding does not typically need the advanced level of skills training needed by more precise or complex welding work.
- Additionally, spot welding
is usually faster than othersorts of welding operations.
Disadvantages of Spot Welding:
- More skilled labor
might be required forthe continued maintenance of spot-welded pieces.
- Additionally, spot welding will not work if the items to be welded are of any vital thickness.
Applications of Spot Welding:
- Spot welding
is sometimes utilized among the manufacture of automobiles, aircraft, Steel household furniture, and steel containers.
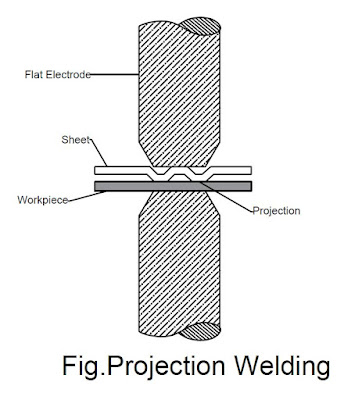
Resistance Projection Welding :
Projection welding joins metal sheets or elements parts using electrodes.
These electrodes are applied to the metal piece items to be joined together. Then, opposing forces are applied through the electrodes.
Advantages of Projection Welding:
- As the welder can weld
quite one spot at a time. Additionally, the welder can position welded spots more closelyto every aside from is feasible with spot welding finally; welds will look somewhat neaterand fewer obtrusive than with spot welding.
Disadvantages of Projection Welding:
- Projection welding can't be used on metals.
- Projection welding can
finish up costing more,thanks to the upper investmentwithin the required equipment.
Applications of Projection Welding:
- Used primarily
within the electrical, automotive, and construction fields.
Resistance Butt Welding :
The heat that's required to produce that connection is created by the electrical resistance that's produced by resistance to the current that's being passed through and between those two surfaces as they face each other.
Resistance Seam Welding :
While some joints have
The
Seam welding
Additionally, seam welding produces joints
Disadvantages of Seam Welding:
- It generally costs more
to realize a seam-welded joint thanit might through other methods.
- Seam welding
is merely appropriate for straight axis seams.
- It
are often difficultto make a joint for any pieces thicker than 3 millimeters.












0 Comments